Understanding Grandfamilies: Nurturing Children Amidst the “10 Ds”
Grandfamilies represent a unique and increasingly common family structure where grandparents or other extended family members step into primary caregiving roles for children and youth. This caregiving arrangement arises when biological parents are unable to fulfill their parental responsibilities due to various circumstances. Among these, the “10 Ds” (a term coined by Dr. Glenda Clare) encompass a range of challenges that can shape a child’s journey into grandfamily care, highlighting the resilience and adaptability of both caregivers and children in navigating these complex dynamics.
The “10 Ds” Shaping Grandfamily Dynamics
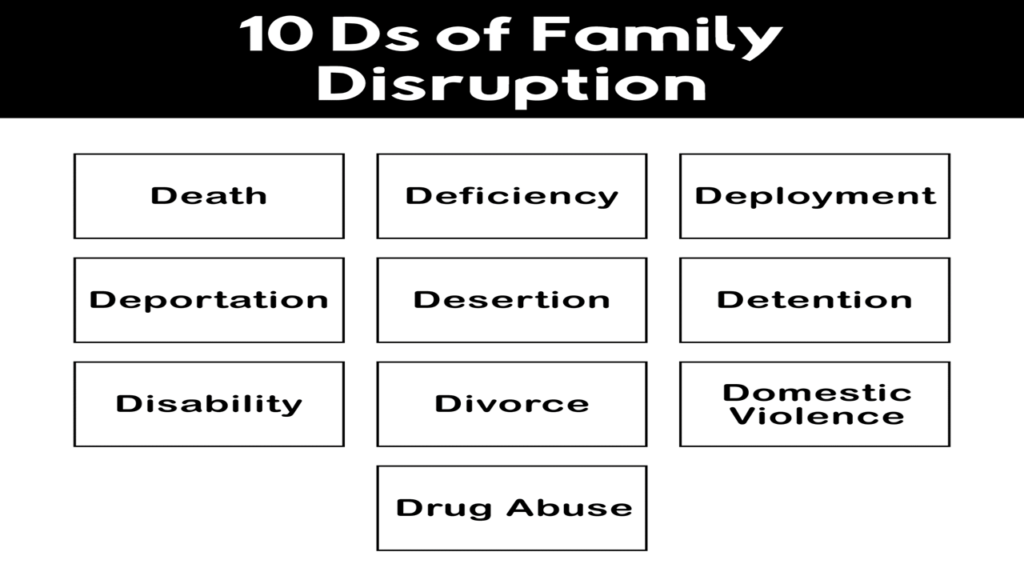
- Death: The passing of a parent can leave children without immediate caregivers, prompting grandparents or other relatives to provide emotional and practical support.
- Disability: Physical or mental health challenges that impair a parent’s ability to care for their children effectively may result in extended family members assuming caregiving roles.
- Domestic Violence: Environments characterized by abuse or violence can lead to protective custody measures, with children placed in the care of safer family members.
- Detention: Parental incarceration can disrupt family dynamics, necessitating alternative care arrangements for children and youth affected by parental absence.
- Disinterest: Parental disengagement or neglect can leave children without adequate care and supervision, prompting concerned relatives to intervene.
- Disability: A parent’s physical or mental health issues may hinder their ability to care for their children effectively, prompting extended family members to step in.
- Divorce: Custody disputes or parental separation can lead to children residing with relatives while parental legal matters are resolved.
- Deportation: The deportation of a parent can abruptly alter a child’s living situation, prompting relatives to provide care and stability.
- Drug Abuse: Substance abuse issues can compromise parental caregiving abilities, prompting extended family members to assume primary caregiving roles.
- Danger: Environments characterized by unsafe conditions or community violence can prompt relatives to take custody of children to ensure their safety and well-being.
Each of these “10 Ds” represents a unique challenge that can significantly impact children and youth, necessitating swift and supportive action from extended family members to ensure their safety, stability, and emotional well-being.
Challenges Faced by Grandfamilies
Navigating the complexities associated with becoming a grandfamily caregiver involves overcoming numerous challenges:
- Legal and Custodial Issues: Establishing legal custody or guardianship can be complex and time-consuming, requiring legal assistance to navigate family court systems.
- Financial Strain: Grandfamily caregivers may face financial challenges due to unexpected caregiving responsibilities and limited access to financial support.
- Emotional Impact: Children and youth may experience emotional distress and trauma due to the circumstances leading to their placement in a grandfamily, requiring sensitive and supportive caregiving.
- Educational Support: Ensuring children’s educational needs are met may require advocacy within school systems, access to tutoring, and resources to address any learning challenges.
Supporting Grandfamilies: Tailored Strategies and Resources
To effectively support grandfamilies and address the diverse needs of children and caregivers, it is essential to implement tailored strategies and provide comprehensive resources:
- Legal Assistance: Offer legal aid and guidance to navigate custody, guardianship, and other legal matters, ensuring caregivers have the necessary authority and support.
- Financial Support: Provide access to financial assistance programs, subsidies, and benefits to alleviate economic strain on grandfamily households, ensuring children’s basic needs are met.
- Healthcare Services: Facilitate access to healthcare, including physical, mental, and dental health services, to address the specific needs of children and caregivers alike.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Establish counseling services and support groups for both children and caregivers to address trauma, adjustment issues, and emotional well-being.
- Educational Advocacy: Advocate for educational resources and support services within school systems to ensure children receive appropriate academic support and enrichment opportunities.
Grandfamilies play a crucial role in providing stability, nurturing care, and a supportive environment for children and youth facing diverse challenges encapsulated by the “10 Ds”. By understanding these dynamics and offering tailored support through legal assistance, financial aid, healthcare access, emotional support, and educational advocacy, we can empower grandfamilies to thrive amidst adversity. Through collaborative efforts and community engagement, we can strengthen the resilience of grandfamily caregivers and ensure positive outcomes for the children entrusted to their care.
©2024 Fragile Families NETWORK







